ASMIS mobileCapture – DICOM Photo and Video App

HCI ASMIS mobileCapture
DICOM Photo Documentation for Tablets and Smartphones in Outpatient Clinics and on the Ward
Another important component for clinic-wide image digitization is the all-new photo app “mobileCapture”. ASMIS mobileCapture is a mobile application for Android and iOS smartphones/tablets, for fast and easy photo documentation in everyday clinical work. Applications such as outpatient wound documentation, e.g. for diabetic foot, or for documentation of decubitus on the ward, require that the patient assignment of the images can be done quickly and easily, e.g. via DICOM worklist or via query in HIS/PACS. Current Apple or Android devices with their very good quality of the integrated camera are ideal for this purpose. The data is sent within the secure hospital intranet, thus meeting all requirements for data protection and data security. The images are sent to the HCI ASMIS server and then to the PACS.
All functionality is provided to the mobile device via the web server in ASMIS. Individual adaptations and functional extensions can be made available centrally to all mobileCapture clients via the HTML code. There is no app-program code stored on the tablets / smartphones, likewise no patient-related data. This ensures data protection even in the event of loss or theft of the smartphone/tablet. ASMIS mobileCapture always requires a secure Wi-Fi connection to the ASMIS server and is therefore not usable on the mobile device outside the hospital intranet.
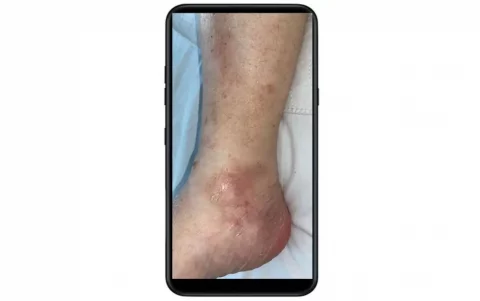
mobileCapture in Wound Documentation
mobileCapture enables the simple and straightforward capture of photos and videos using mobile devices, allowing them to be made directly available in the patient record — for example, for nursing- and wound-documentation.
- Patient data is provided via a DICOM worklist and easily transferred to the smartphone or tablet.
- The clinician uses the built-in camera to photograph the affected wound areas.
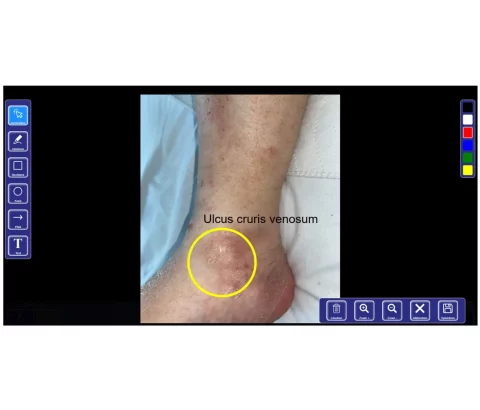
Structured Documentation
Each captured image can now be annotated directly on the mobile device by the examiner using graphic markers (colored circles, rectangles, arrows) and short text notes.
To do this, the user can open a predefined library of text modules or keywords via a dropdown menu and insert the relevant term directly. This ensures structured, semantically clear and consistently defined tagging. Typing errors are eliminated, and the time required is reduced to a minimum. The contents of this text module/ keyword library can be created or modified by the clinician at any time and are then automatically available to all users.
In addition, a “Suspecious Case” button is available here, allowing the examiner to mark situations that are not clearly identifiable. All studies and images marked as “Suspicious Case” can later be accessed directly for review and clarification by a colleague as a second opinion.
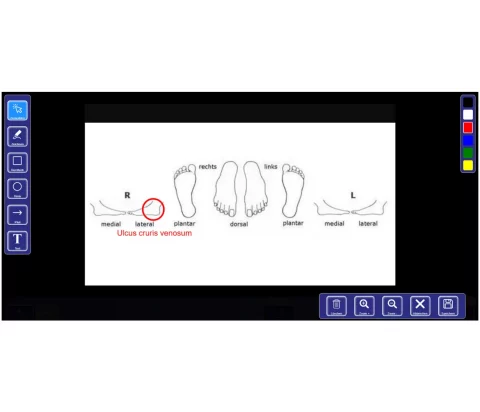
Use of Body Maps
If more extensive image documentation of the case is required, or for additional visual clarification, the examiner can also open a body map – provided as a predefined file – on the mobile device.
Here too, the described annotation and keywording tools are available. This body map function can also be used, if needed, to clearly identify the task assigned to the next staff member or examiner. Manually filling out a paper-based work order is no longer necessary.
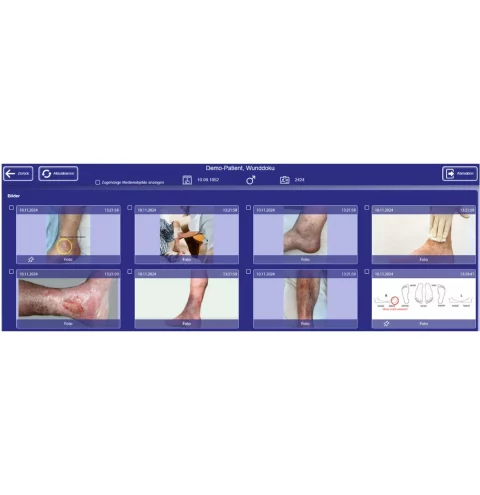
Case Overview and Additional Documentation
All clinical imaging media for the respective patient are now available on the ASMIS server for viewing and further processing, clearly displayed in the ASMIS web client. In addition to ASMIS’s powerful search and editing functions, further clinic-specific features are available:
- Direct display of all studies and examinations that could not be clearly diagnosed by the initial examiner and were therefore marked as suspicious cases
- Access to a clinic-specific keywording dictionary, allowing individual images to be labeled with phrases or terms (via the ASMIS Info Pin), or to mark the region of interest within an image using annotation tools
- Automatic transfer of images and report annotations / Info Pins to the PACS
- A “Teaching & Research Study” function marks a patient study as relevant for research and documentation purposes and transfers the media content and metadata—anonymized—into a dedicated storage level provided by the clinic. This “third-party transfer” to a VNA or network storage can also be defined by rule and executed automatically
- Manual and anonymized download of studies or individual media objects to a local client PC or USB stick
- Anonymized provisioning of studies or individual media objects in the internal ASMIS share area, with access granted to authorized clinical users via URL call

Supported Mobile Operating Systems and Resolutions
Tablets and smartphones with Android
Resolution of still images: Max. resolution of the device camera for images
Resolution of videos: Max. resolution of the device camera for videos
Apple tablets and smartphones with iOS
Resolution of still images: Max. resolution of the device camera for images
Resolution of videos: 480 x 360 pixels